AI compute has become a geopolitical asset, and Web3 could be the loser, a report by O.XYZ explains.
Summary
- O.XYZ report shows how the high cost of AI hours is pricing out Web3 devs
- Geopolitical realignments are further driving AI costs
- Regional costs of AI compute remain highly dispersed
Geopolitical realignments are making AI too expensive for most Web3 developers. According to an O.XYZ report published on Thursday, August 14, AI compute has become a geopolitical asset, and countries are fighting for control over it.
The report shows that chips are no longer the only bottleneck for AI. Even as Nvidia GPU prices cool, infrastructure remains one of the major limitations for large-scale AI deployment.
Due to increased demand, data center infrastructure is at its limits in certain regions. This is evident from Amazon’s “Project Greenland,” which restricts the deployment of compute-intensive services in select areas. This scarcity also translates into wide differences in the regional cost of AI compute, with price spreads as high as 6x.
“Compute has become a geopolitical asset,” says Ahmad Shadid, Founder & CEO of O.XYZ. “Web3 projects that ignore the new geography of chips, power, and law will find themselves yoked to centralized gateways. Survivors will be those who plan for scarcity, verify hardware and content, and diversify across jurisdictions.”
The AI industry is splitting on geopolitical lines
The report shows that AI chip production has fractured into three main blocs, each increasingly independent from the others. One is the U.S.-aligned bloc, dominated by Malaysia and Thailand, which enjoys privileged access to the U.S. market.
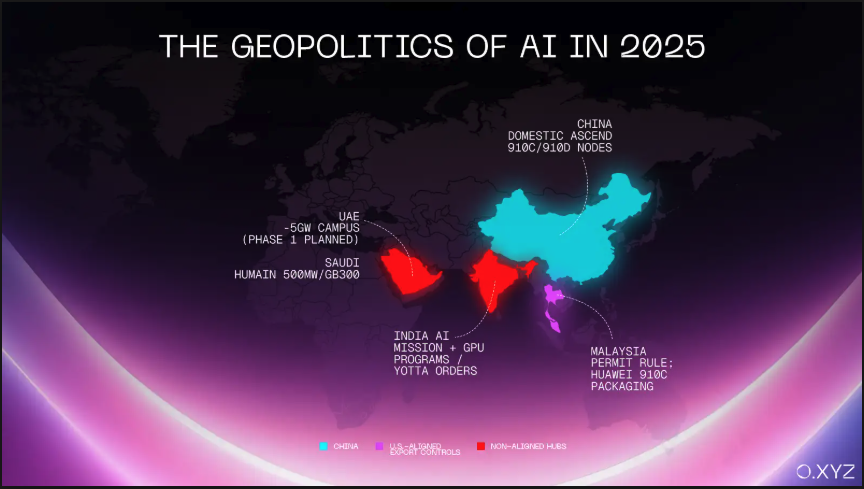
On the other hand, China is scaling up its own production of AI chips with Huawei’s Ascend 910C and the CloudMatrix cluster. Meanwhile, the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and India are building their own bloc.








